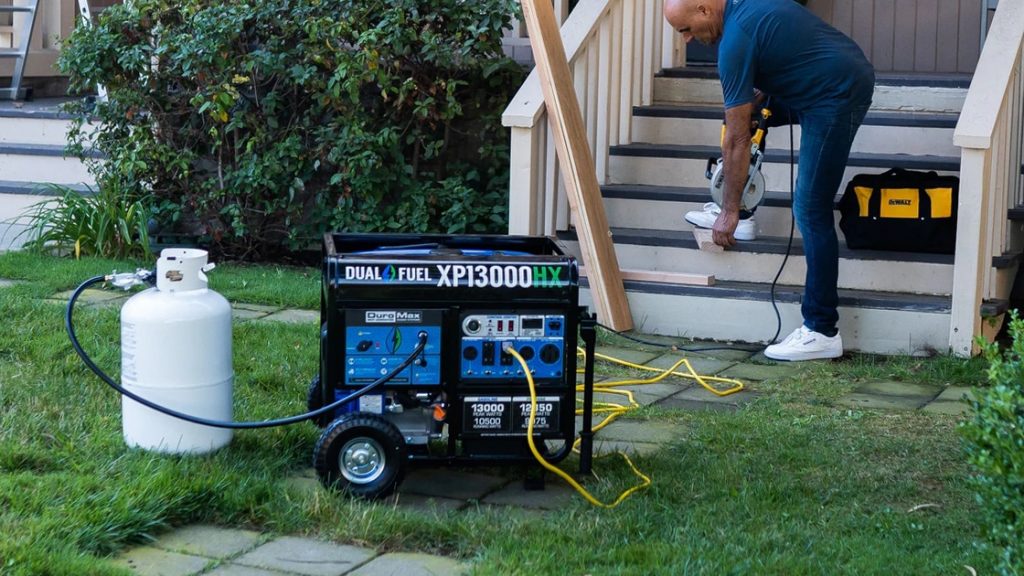
When the electricity fails, an emergency generator can keep your house running, and you won’t be left in the dark. But what size generator for a house?
The generator is available in different wattages, from 2,000 to 20,000 watts. You can choose the right size after considering what appliances you need.
We will discuss the generator sizes and how to choose the most suitable option right here. Let’s read on to discover!
What Size Generator For A House Do You Need?
The generator comes in five different sizes. Each option has a different electricity output and price tag, serving specific purposes.
So, what size generator do I need? Let’s check the options one by one and consider your situation to choose the best one.
Recreational Inverter
- Capacity: 2,000 watts
- Price: $400 – $1,000
- Best for: On the move
This type is the lightest form of generator, with an electricity output of up to 2,000 watts. It costs about $400 to $1,000 and weighs roughly 60 pounds.
This portable engine works quietly. It doesn’t require any setup. Moreover, inverters for recreational usage are often user-friendly, with many versions featuring phone apps.
Please remember that, although recreational inverters may cost as much as portable ones, they produce far less power, capable of just powering a fridge, lights, and small devices.
If you’re on the move, if your house rarely loses electricity, or if you want something compact, a recreational inverter is a nice choice.
Mid-Sized Inverter
- Capacity: 3,500 watts
- Price: $1,000 – $1,600
- Best for: Homes with few blackouts
This machine stays true to its title, with up to 3,500 watts, a price range of $1,000 to $1,600, and a weight of 150 pounds.
Like the recreational version, it’s quiet and lightweight. The difference is that it can handle more power.
A mid-sized generator can power lights and a refrigerator, helping them work for 18 hours.
However, this machine will not be able to power everything. Most can only operate 110-volt appliances with regular two- and three plugs.
As a result, you’ll have to search elsewhere if you need to run the cooling or heating systems and pumps.
This model is a perfect choice for individuals seeking backup generators in a house with few blackouts.
Its capacity to power necessary facilities for extended periods will help ease the pain while keeping your home running smoothly.
1. Mid-sized inverters are enough for homes with few blackouts
Portable Generator
- Capacity: 7,500 watts
- Price: $700 – $2,700
- Best for: Homes with regular blackouts
This generator is the highest value, with a power output of 7,500 watts and a price range of $700 to $2,700.
Please note that the name of this machine may be confusing since most units weigh over 300 pounds.
Most portable generators generate sufficient power to cover the needs of an average home. You can also connect them to a breaker panel to energize hardwired equipment such as pumps.
It’s worth noting that wiring this machine to your house’s circuit breaker might be as expensive as the engine itself. Besides, this unit can’t work in the rain or snow without adequate protection.
These products are an excellent addition for houses that suffer power outages regularly. They are durable and cost less than a thousand dollars.
2. You can connect the inverter to a breaker panel (Link)
Large Inverter
- Capacity: 7,500 watts
- Price: $1,400 – $4,000
- Best for: Homes with frequent and lengthy power failures
With an energy capacity of 7,500 watts, this unit costs $1,400 to $4,000. It weighs 250 to 350 pounds.
Large generators can power items such as a refrigerator and a small air conditioner at the same time.
These units are also fuel-efficient and quiet, providing consistent power for more delicate devices.
Another thing to note when using this generator is that it needs stabilized gasoline to work instead of propane or natural gas.
Because of their stability and capacity to support essential appliances, these units are ideal for houses that endure frequent and lengthy power failures.
Home Standby
- Capacity: 20,000 watts
- Price: $2,000 – $6,000
- Best for: Homes with frequent power outages and lack of electricity access
If you wonder what size generator to run a house, this product is the most common choice.
Home standby generators are permanent machines that provide up to 20,000 watts of power. They cost from $2,000 to $6,000 and weigh between 350 and 600 pounds.
During a power failure, the unit automatically turns on. It delivers a steady current of electricity to all of your gadgets.
The home standby generator is the most convenient model for household usage. Yet, it also usually costs the most.
The cost of installing this unit can be as high as the unit itself, making it a highly expensive solution for some.
If you live in a flood-prone region, this model is not ideal because you can’t install it in wet places and move it during the flood.
Meanwhile, if you live in a region where power outages are often or don’t have electricity access, a home standby generator may be the most practical option.

3. This unit can power a house (Link)
Related:
- Ultimate Guides To Choosing The Right Generator Fuel Type
- What is an inverter generator?
- How to maintain a generator
- Inverter Generator Vs Generator – Which Type Should You Buy?
How To Choose A Generator To Run A House?
As you can see, there are five options for generators for houses. So what size generator do I need for my house?
It would be best to consider different factors, such as the appliances you want to power and their wattage. For a detailed guide, please scroll down.
Step 1: List the appliances you want to run
If you need to power your house, make a list of all the essential items you want to keep running in the event of a power failure.
This list should cover the fridge, freezer, air conditioning, and lights circuits. You can also add devices for entertainment, such as a TV or DVD player.

4. List what you want to power (Link)
Step 2: Understand starting, running, and surge wattage
The generator’s watts, or power, are contingent on the number of gadgets or appliances to run. There are three figures you need to pay attention to.
- Starting wattage
As the name implies, this figure refers to the wattage needed for a device to start. It is usually two or three times more than the running wattage.
Many electrical equipment and appliances demand greater energy to warm up and less power to keep working.
When the electricity goes out, a generator has to cope with a spike from all of the always operating appliances, such as the water heater, fridge, freezer, and HVAC system.
If a microwave, dishwasher, or washing machine is in use during the disruption, the generator will also have to power these.
- Running wattage
Running wattage, also known as rated wattage, refers to the power required to keep an electronic gadget or appliance operating.
Many devices list this figure on their package to assist in determining how much wattage is necessary to power things.
When choosing a generator, the running and starting wattage of the appliance are the two most important figures to check.
A regular 10,000 air conditioner uses 2,200 starting watts. During the first seconds, 2,200 watts is how much it requires to start up.
After that, its energy consumption decreases, demanding a steady input of 1,500 running watts.
As a result, to power the AC, the generator must be able to handle 1,500 – 2,200 watts. You can learn more about the starting and running wattage right here:
- Surge wattage
Surge wattage is the maximum amount of watts that a generator can deliver.
If you wish to use the engine to supply all of your devices and appliances, you need to add 1,000 to 2,000 more watts to withstand the initial spike.

5. The running, starting, and surge wattage of an appliance are different (Link)
Step 3: Understand Watts vs. Amps vs. Volts
Electric current is the total energy that runs across a wire over a certain length of time, and you may measure it in different ways.
You can identify the differences in electrical equipment after figuring out the difference between amps, volts, and watts.
Consider the flow of electrons in the same way that water does in a river. Voltage is a unit of measurement for the electricity between two places.
The voltage differential between two points occurs when a charge moves from one point to the other.
Voltage always goes from a high value to a low value, similar to how a river flows from a high position to a low one.
The strength of a charge streams in amperes, or amps. In the river example, amps represent the amount of water that flows through a specific point in a given amount of time.
Volt-amperes, or VA, is a unit of measurement that combines volts and amps.
The objective of a generator, on the other hand, isn’t simply to generate power for the sake of it; it works as a functional energy source, such as heat and light.
The current generated by this engine and entering your home will power anything it connects to.
Wattage is a measurement of how much energy a gadget uses. The formula for calculating watts: Wattage = Voltage x Amps.

6. Understanding the measurement unit of electricity is important (Link)
Step 4: Calculate the approximate power requirements
How to calculate what size generator I need? This task involves checking your list of appliances and calculating their wattage.
What size generator to run the refrigerator and freezer? You can find electrical information should be rather straightforward. There will be a tiny panel on the back of most devices with the make and model and other important details.
Try seeking up a user’s handbook for each device in the records or on the internet if you can’t see it or it has faded.
After that, total up the wattage of all of the gadgets. The result is a great starting point, but it’s probably a little more than you’ll use for a generator.
After all, it’s quite rare to power all of the appliances at the same time. Hence, consider how often you need them all.
For example, you don’t run the washing machine and dishwasher simultaneously. Hence, when calculating the wattage, you can choose one of them.
Here is a chart of approximate power requirements for a home’s appliances:
| Appliance | Starting wattage | Running Wattage |
| Refrigerator | 2,200 | 700 |
| Air conditioner | 2,200 | 1,500 |
| Microwave | 1,300 | 1,300 |
| TV | 120 | 120 |
| Freezer | 1,500 | 500 |
| Hot water heater | 4,500 | 4,500 |
| Laptop | 250 | 250 |
| Lightbulb | 60 | 60 |
| Dish washer | 540 | 216 |
| Garage door opener | 1,420 | 720 |
| Box fan | 200 | 200 |
| Hair dryer | 1,900 | 1,800 |
| DVD player | 350 | 350 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 800 | 800 |
| Slow cooker | 250 | 250 |

7. Each item has a certain power requirement (Link)
Do You Need To Power Your Entire House Or Just Some Essential Appliances?
The answer depends on your requirement. Do you want everything, or just some of them to work normally during the blackout?
The generator you use also affects your decision. For example, using a standby model will allow you to power all the appliances.
On the other hand, if your machine has a lower output, you can only work with some gadgets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Homeowners have shown their concerns when looking for generators. Here are some questions.
1. What size generator to run central air?
The average central air conditioner requires around 3,500 watts of power. When choosing a generator to go with this requirement, go for one with a power output of 6,000 to 6,500 watts.
2. What size generator to run a 3-ton AC unit?
A 14-KW generator can handle a 3-ton (30-amp or 36,000 BTUs) air conditioner.
3. What size generator do I need for my RV?
Generators for RVs typically range from 2,000 to 4000 watts, although they may go up to 12,000 watts. In certain cases, bigger is better, but it’s heavier, louder, and less fuel-efficient.
4. What size generator do I need for my camper?
Some RVs feature 30-amp power, while others have 50 amps. The difference is in the amount of electricity the RV can use based on the voltage and amperage.
Multiply the number of volts by the number of amps to get the total sum. Because the total is 3,600 watts, the largest generator you may utilize is a 3,600-watt engine.
Conclusion
To figure out what size generator for the house you need, you can list the appliances you want to work with and total up the required wattages.
There are a lot of choices. You can relate to the calculated value and your preference to determine the best generator for your needs.
Hopefully, you will find this guide helpful. For any further information, please feel free to ask. Thank you for reading!


